ACID-BASE PROPERTIES OF NITRILES
The basicity of a nitrile group can be studied from the acidity of its protonated form.
A protonated nitrile is extraordinarily acidic and consequently its nitrogen is much lower basic than that of an aniline or amine.
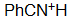 Benzo-nitrile
Benzo-nitrile
pKa = -10.0
The nitrogen's electron pair of a nitrile dwells very close to the nucleus in a sp orbital thus being very unaccesible.
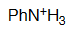 Aniline
Aniline
pKa = 4.6
The nitrogen's lone elecron pair of an aniline is partially delocalized towards the ring, thus making it less basic than an amine's or, conversely, making an anilinium cation more acidic than an ammonium one.
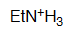 Ethylamine
Ethylamine
pKa = 10.6
The electron pair on an amine group is fully localized and therefore they are the most basic of this series.
The alpha hydrogens to a nitrile are feebly and scarcely usefully acidic, due to the poor delocalization of the negative charge towards the CN group.
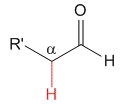 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
pKa = 17
Aldehyde's hydrogen does not exert any special effect and pKa = 17 can be taken as a reference acidity value for the alpha hydrogens to a carbonyl group.
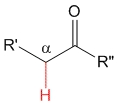 Ketone
Ketone
pKa = 20
Alkyl groups are electron releasing by inductive effect and therefore they destabilize the anion, thus making ketones' alpha hydrogens less acidic than aldehydes'.
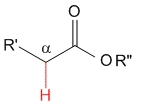 Ester
Ester
pKa = 25
Alkoxy groups are strong electron releasing by mesomeric effect and destabilize the anion even further, thereby causing the lowest acidity for esters in the studied series.
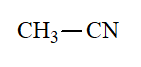 Nitrile
Nitrile
pKa = 31
The CN group bears the lowest capability to stabilize a negative charge generated at the alpha position.
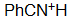 Benzo-nitrile
Benzo-nitrile
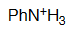 Aniline
Aniline
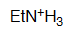 Ethylamine
Ethylamine
 Aldehyde
Aldehyde
 Ketone
Ketone
 Ester
Ester
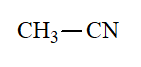 Nitrile
Nitrile